Basics of hexagonal architecture + Project
Getting started with hexagonal architecture with simple questions
What is hexagonal architecture?
Documented in 2005 by Alistair Cockburn, hexagonal architecture is a software tool which has a lot advantages and got your interest renewed in 2015.
Why to use it?
To allow a application be equally driven by users, programs, automated tests or batch scrips and develop or tested in a totally isolated form from your devices and databases
A picture from how that architecture achieves that
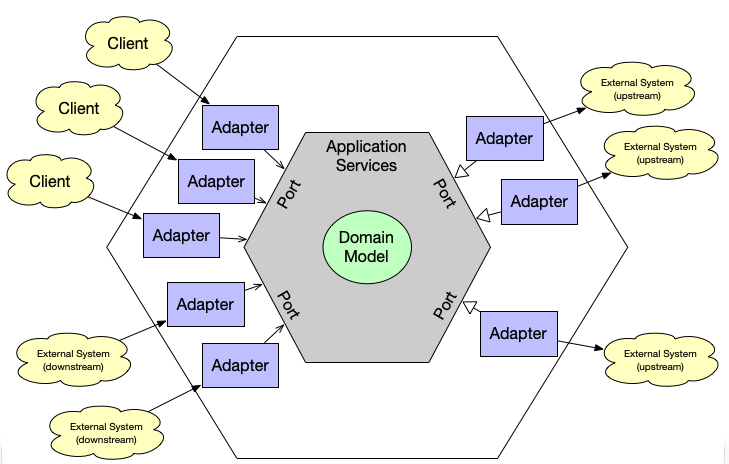
- Domain layer:
- The mains reason of the software existence
- Entity
- Business logic
- Application Layer:
- Use cases
- Application flow
- Framework Layer (adapters):
- Serialization
- HTTP
- Visualization process
- Domain layer:
The main reason to use it
- To isolate the core (Domain and application) as much as possible from the the framework layer
How does the application communicate with the other parts?
Through ports (like Interfaces in Java) and adapters, which are implemented in these ports
Adapters stays outside of the core, which means that can be easily replaced at any time
Inbound communication
- When an action is required from outside of the core. Example: Any requisition from a browser
Outbound communication
- When an action comes from inside of the core. Example: Persisting any data on the Database
The difference between the traditional layers architecture and hexagonal architecture
- In the hexagonal architecture, there is no coupling between the core and the infrastructure
Pros
- It’s easy to code unit tests
- Independent of frameworks or other tools
- Low or no coupling in the application core
- It’s easy to replace any part of the infrastructure, like a database
Cons
- Additional complexity
- There is no organization standards to work with that architecture
Personal project using hexagonal architecture
To deepen my knowledge, I coded an API in Java which is totally uncoupled from the frameworks, you can find it here: Breaking bad API
At the beginning, I was struggling with interfaces and the communication between the domain layer and the framework layer, but I had a help from Gabryell who I’m grateful
Source:
ARQUITETURA HEXAGONAL EM MICROSERVICES (Portuguese) - Michelli Brito